West Africa is home to the world’s most violent pirates—who are now proving capable of overwhelming armed guards. Last month pirates killed a crewmember during an attack on German-owned oil tanker. Instead of fighting off the pirates, the embarked security team retreated to the ship’s citadel safe room.
For the shipping and insurance worlds, the widespread adoption of armed guards aboard vessels essentially ‘solved’ Somali piracy, as no vessel employing them has been hijacked by pirates. An attempt to transfer this panacea to the pirate-prone waters of West Africa, however, has proven inadequate and ill-suited to local conditions.
On the night of April 29, pirates attacked SP Brussles 35 nautical miles off the coast of Nigeria. Local security forces guarding the vessel were unable to prevent the pirates from boarding and retreated to ship’s citadel along with the crew. The guards did not emerge until the following morning, only to find that the ship’s chief engineer had been killed and another crewmember injured as they failed to reach the citadel.
This incident and others like it highlight three important issues that distinguish West African from maritime crime in other parts of the world.
First is the distinctive operating environment in which international naval patrols are absent, the response capacity of regional security forces is limited, and the use of foreign armed guards is prohibited.
Second, is the uniquely violent nature of Nigerian pirates and their propensity to engage in shootouts with security forces.
Finally, are the multiple shortcomings of using local armed guards aboard vessels and the inherent danger the shipping industry faces in being overly reliant on this measure.
Getting Around the Neighborhood
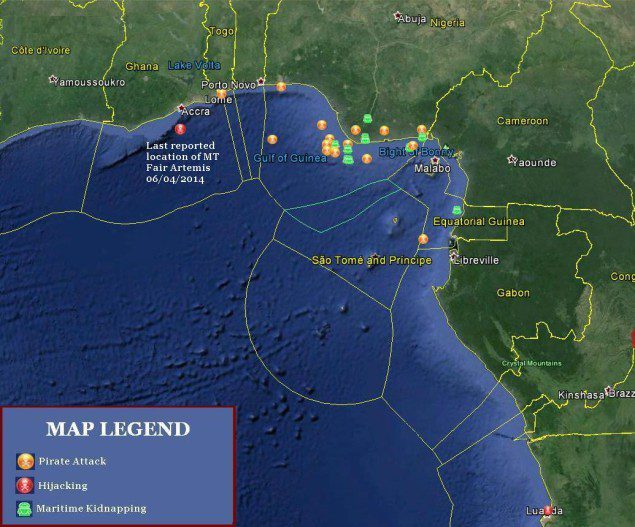
Piracy in the Gulf of Guinea is a Nigeria-centric problem that primarily occurs within 100 nautical miles of the coast and targets the ships plying the regional oil trade. Local naval forces have provided a modicum of security for transiting vessels, but their ability to respond to pirate attacks outside of territorial waters and secure anchorages is limited. The pirate’s proximity to shore coupled with local concerns over state sovereignty has prevented international naval operations from deploying as they have off Somalia.
These same confines have restricted Private Maritime Security Companies (PMSCs) from operating in the region as national laws prohibit foreign guards from carrying weapons within the 12nm limit of territorial waters. For embarked security, shipowners are forced to rely on armed guards contracted from littoral states. These guns on deck, drawn from national police and naval forces, are often poorly trained and undermanned, making them ill equipped to match the threat they face.
Ultraviolence
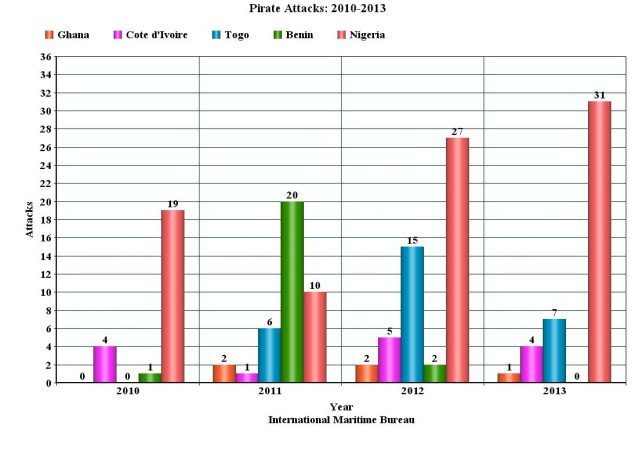
A recent UN report found that pirate attacks in West Africa from 2006 to 2013 have been proportionally more severe (involving vessel hijacking, hostage taking and violent acts towards crew members) than those in the Western Indian Ocean and South East Asia. West African pirate attacks have also become more violent over time, the report notes, particularly from 2011 onwards. International Maritime Bureau data records show more crewmembers were injured and killed off Nigeria than other country from 2012 to first quarter of 2014.
Regionally distinct pirate ‘business models’ partially explain this phenomenon. When Somali pirates hijack a vessel, they must ensure that the hostages are kept alive so that ransom negotiations for the return of the entire crew and ship can proceed smoothly.
West African hijackings, by comparison, are usually “extended duration robberies,” in which the crew and vessel are only held hostage until the ship can be pumped of its petroleum cargo. When maritime kidnappings occur, pirates take only the most valuable (usually Western or Asian) officers for ransom while leaving the rest of the crew and vessel behind. Under both scenarios, the majority of the crewmembers hold no value for the pirates and are thus considered disposable assets.
Armed to the Teeth
West African pirates are also better armed and trained than other maritime criminals, reportedly wielding heavy machines guns, such as M60s, and RPGs. Many of these weapons are ‘legacy firearms’ circulating from previous African conflicts, while others are sold or rented from corrupt security forces.
This heavy armament is a product of the pirate’s proximity to their onshore bases in the Niger Delta, which allows them to carry more weight in weapons and ammo and less in fuel and water than their Somali counterparts. Nigerian pirates also display military-grade tactics, explains Kevin Doherty, Owner of PMSC Nexus Consulting, “they know how to skillfully maintain and fire their weapons, they ambush security forces, and they board vessels with tactical precision.”
The weapons and tactics displayed by the pirates are often superior to those of the security personnel hired to protect vessels, notes a report from the counter-piracy think tank Oceans Beyond Piracy. As a result, local soldiers contracted to guard ships have reportedly hidden during pirate attacks. “They hide, just like that,” exclaimed a regional seafarer, “When we ask them why they hide, their answer is simple, ‘The weapons of rebels and pirates are stronger.’” An alternative, often anecdotally reported explanation is that naval guards have colluded with pirates in exchange for a share of profits.
Nigerian pirates are often undeterred by onboard security forces and willing to use deadly force to achieve their objectives. While shootouts between pirates and embarked security are exceedingly rare in the Indian Ocean, they are becoming increasingly common in the Gulf of Guinea, resulting in multiple casualties.
| Fatal Nigerian Pirate Attacks 2012-2014* |
| Date & Location |
Incident Details |
Casualties |
| February 13, 2012100 nm South of Lagos, Nigeria |
Pirates fired on, boarded, and robbed a drifting bulk carrier, MV Fourseas, off the coast of Nigeria. The pirates killed the ship’s Master during the robbery, while Chief Engineer died from injuries sustained during an attempted escape. |
Master and Chief Engineer killed. |
| August 3, 201245nm SW of Bonny Island, Nigeria |
Pirates armed with AK 47s overpowered the Nigerian naval personnel guarding an oil barge, Jascon 33, and kidnapped four crewmembers for ransom. |
Two Nigerian guards killed, two guards injured, four crewmembers kidnapped. |
| December 13, 201225nm SW offshore, Bayelsa, Nigeria |
Pirates armed with machine guns attacked an offshore supply vessel, PM Salem, and engaged in a 20-minute firefight with onboard security guards before retreating. |
One Nigerian guard killed, one guard injured. |
| February 4, 2013Lagos Anchorage, Nigeria |
Pirates attacked and boarded an anchored chemical tanker, Pyxis Delta, conducting STS operations off Lagos. The onboard naval security returned fire and eventually repelled the attackers. |
One crewmember died from injuries sustained during the firefight. Two pirates were also killed. |
| February 5, 2013Near Angiama, Niger Delta waterway, Nigeria |
Gunmen ambushed an Indian-owned oil barge as a Nigerian military detachment escorted the ship through the Niger Delta. |
Two Nigerian soldiers killed, one crewmember killed, three crewmembers wounded. |
| April 29, 201435nm W offshore Bayelsa, Nigeria |
Armed pirates boarded a product tanker, SP Brussels, underway. The onboard security forces fired at the pirates before retreating to the citadel along with most of the crew. |
Chief Engineer killed, Third Officer wounded. Two pirates were also killed. |
The Wrong Answer
Armed guards aboard ships in West Africa do not provide the silver bullet security solution that PMSCs have in the Indian Ocean.
A key differentiator in the latter theatre is that ship owners have a number of tools for vetting the quality and compliance of the armed security they hire.
For example, the GUARDCON contract developed by BIMCO, the largest international shipping association, provides a standard agreement between ship owners and PMSCs that covers guidance on Rules of Force and other security issues. In addition, there is the ISO/PAS 28007 accreditation that allows PMSCs to certify their compliance with appropriate regulations and best practices.
Vetting and compliance is much more problematic in West Africa as vessel owners and Masters have far less oversight over the armed guards they bring aboard. Owners can either hire security forces directly through a local agent, or engage a PMSC to act as an intermediary to employ local guards and provide unarmed logistical support and leadership. In either case, BIMCO notes, the local security forces will operate under their own rules of engagement and cannot be bound to the provisions of GUARDCON.
When a vessel contracts local security, it is the soldiers’ commander, not the shipowner, who usually controls the number of guards posted. An undermanned and poorly drilled guard team bears responsibility for the fatality aboard the SP Brussels, argues Rene Toomse, CEO of the PMSC Aburgus. “What was missing,” Toomse explains, “was a guard assisting all the crew into the citadel while others were fighting with the criminals.” The vessel had only two armed guards onboard at the time of the attack, rather than the BIMCO recommended staffing of four.
Maritime insurers and PMSC owners have privately expressed reservations that an overreliance on onboard guards is contributing to lax safety and security standards in West African waters. One source close to the London insurance market noted a particular problem of vessels with embarked security rejecting advisories to avoid prolonged exposure in high risk-areas close to the Niger Delta, opting instead to save time and fuel by using shorter routes and “shooting their way out” of any potential pirate attacks. The majority of these incidents, it was further noted, are never reported to authorities and thus contribute to a cycle of inaccurate threat perceptions and inadequate security measures.
Multiple Layers
It is very unlikely that the laws barring foreign armed guards from West African territorial waters will change, despite pressure from PMSCs and shipping organizations. Concerns over sovereignty and control understandably run deep, particular in Nigeria, and the current regime of renting local guards to foreign ships is too lucrative to give up. Unarmed PMSC advisors working with local guards offers an improved measure of security, but BIMCO still warns that the ability of PMSC leaders to effectively control their teams will be limited.
As no single defense against West African piracy is impenetrable, a multi-layered security system must be implemented. This begins with a pre-transit risk and security assessment and requires up-to-the-minute information on pirate activity and vessel vulnerabilities. Communication security is also essential, as pirates are known to select their targets by obtaining route and cargo information from open and private sources. Vessel hardening measures such as the use of citadel safe rooms are key, but it is also imperative that crews are regularly drilled for emergencies. Vessels also need a well-staffed 24-hour watch duty as West African pirates primarily attack at night.
Even with all these measures in place, the most important lesson to draw from the SP Brussels and other fatal pirate attacks is that no vessel should ever be lulled into a false sense of security.
James M. Bridger is a Maritime Security Consultant with Delex Systems Inc. in Herndon, VA. His current areas of focus and expertise address piracy, terrorism, and other irregular threats to global maritime transportation. He can be reached at jbridger@delex.com